At the back end of last year I saw an excellent presentation on blockchain, a technology I have tried to keep an open mind on. But this talk kind of confirmed all my fears. Let me take you through the key parts of the talk and then I’ll leave the comments open to see whether you all come to the same conclusion or can point out what I’m missing.
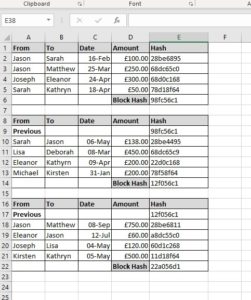
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology.
A ledger is a essentially a list of transactions.
A hash is created for each transaction, a value that is unfeasible to reverse. So it verifies the transaction hasn’t been changed. If you then hash a “block” of these transactions with a hash record together you get a block hash. Then if you add each block hash to the next you get a ….. chain.
Then distribute these ensuring the chain is agreed between them all, the more copies the harder it is to change or fake the ledger.
That’s blockchain and so far seems pretty useful as a way of protecting data?
But if the ledger cannot change and isn’t regulated then errors cannot change either right?
But it’s good for smart contracts right? The blockchain tech makes the contract unalterable. But a bug in the code and, well back to the point that the block chain makes the contract virtually unalterable ie impossible to unpick! (something that has happened)
All technology has issues, so I get this is not a reason to dismiss the concept. But unless you have zero trust in other parties and require unalterable data and where regulation or law doesn’t help, I can’t help think a standard secure database can do the job you’re after?!
Pretty much what the Australian Government said, this is a quote from Peter Alexander, Chief Digital Officer at Australia’s Digital Transformation Agency : Oh and one more reason blockchain technology like bitcoin may not be worth pursuing : “Bitcoin Mining Now Consuming More Electricity Than 159 Countries Including Ireland & Most Countries In Africa” source
Oh and one more reason blockchain technology like bitcoin may not be worth pursuing : “Bitcoin Mining Now Consuming More Electricity Than 159 Countries Including Ireland & Most Countries In Africa” source
To me the key question then is simply why do you need a distributed ledger, especially laws firms as it kind of removes the need for them in the transaction. If both parties agree a contract on a distributed ledger, you’re pretty much saying it doesn’t matter if we don’t trust the other we’ve an unalterable contract without the need for a middle man. Maybe it just shifts everything from transaction law to litigation? And if you actually still need the lawyer to create the contract then why not just put it in a secure database of the law firm?
Thoughts?
Oh and a big credit to Paul D Johnston who’s original presentation on what is blockchain was the jump off point of pretty much all of the above!